Menagesha Medhane Alem
The Menagesha Medhane Alem Monastery forest is a
relatively species rich stand in the close vicinity of Addis Ababa. Although it
is not affected by herbivory, there is hardly any natural tree regeneration and
the shrub layer is scarce whereas the herbaceous layer is dense. The spread of
invasive species, regenerating profusely in the surrounding plantations and
native scrub, is the main threat confronting this forest.

Menagesha Medhane Alem 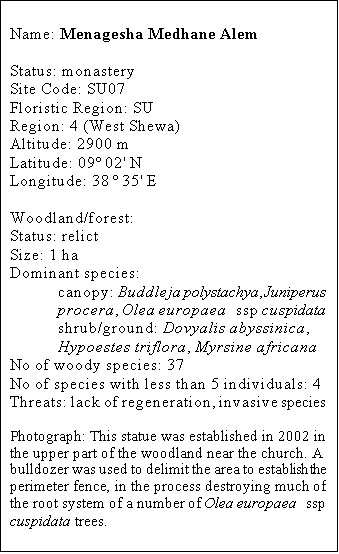 is situated on the top of an extinct volcano to the West of Addis
Ababa. This small hill dominates the surrounding countryside and in places its
slopes consist of sheer cliffs.
is situated on the top of an extinct volcano to the West of Addis
Ababa. This small hill dominates the surrounding countryside and in places its
slopes consist of sheer cliffs.
On the gentler slopes most of the vegetation consist
of forestry plantations mainly dominated by
Cupressus lusitanica. On steeper slopes there is an Erica arborea dominated scrub. The native forest, that formerly
dominated most of the hill, is now restricted to an area close to the summit.
It is totally surrounded by exotic tree species some of which have also been
planted across the native stand. The canopy of the native forest is open in
places. The ground layer is dense and often dominated by grasses, whereas the
shrub layer is scarce or totally absent.
On the slopes of the nearby and much larger Wuchacha
Mountain there is a large block of forest dominated by native species. This
forest was planted some centuries ago. However, in the vicinity of Menagesha
hill the woody vegetation is dominated by plots of eucalypts with very few
native trees remaining.
History
The establishment of the Menagesha Medhane Alem monastery
is relatively recent. However, the site has been linked with a nearby church
situated at the base of the hill. For the pasts three decades the area of
natural woodland has been under the jurisdiction of the state and not the
church. Forestry in the area has been essentially concerned with the
establishment of exotic plantations. The native stand is part of the State
forestry plantations.
Conservation status
This site, considering its
small size, is relatively species rich and has a few large native trees left.
The stand could provide a good seed source for a number of local species.
Threats
Unlike other
investigated sites grazing by large herbivores is not a threat at Menagesha.
Although not affected by grazing this woodland has very limited natural tree
regeneration, probably in many parts of the wood because of the dense ground
layer. The small size of the woodland is also a cause for concern.
Exotic species are
regenerating freely in the surrounding plantations. Of particular concern is Acacia decurrens, this species is
rapidly spreading into the remaining nearby natural stands of Erica arborea dominated scrub.
The use of a bulldozer
to delimit of area to be fenced off around the statue erected in 2002 (see main
photograph), and its destruction of part of the root system of canopy trees
illustrate that trees may easily be damaged or even destroyed for religious
purposes.
Management
Although the dense
ground vegetation hinders natural regeneration of native trees it does,
however, appear to prevent the spread of invasive species. Any reduction in the
density of the ground layer, e.g. through grazing, would promote the
establishment of invasive species and Acacia
decurrens in particular. Unless invasive species are dealt with over the
whole hill, all attempts at regenerating the natural woodland using appropriate
silvicultural techniques will favour exotics. The planting of the rarer canopy
species, using seedling produced from local seed source, in canopy gaps should
be envisaged.
As the natural stand
is part of the Menagesha Forest the church has no ability to initiate and
implement any management policies.

 is situated on the top of an extinct volcano to the West of Addis
Ababa. This small hill dominates the surrounding countryside and in places its
slopes consist of sheer cliffs.
is situated on the top of an extinct volcano to the West of Addis
Ababa. This small hill dominates the surrounding countryside and in places its
slopes consist of sheer cliffs.